Formula 1 is recognized as the pinnacle of motor racing, featuring cars designed for extreme speed and power.
At the heart of every F1 car is the engine, the key part that drives performance on the track. Many fans are curious about the engines used in F1 cars and how they work.
The story is not simple, as engines have undergone significant changes over the years.
Today, Formula 1 cars run with advanced hybrid power units that balance speed, fuel use, and reliability.
Teams must adhere to strict rules while striving for optimal performance. Engines are designed to withstand the rigors of intense racing while still delivering top results.
This guide explains the engines used in F1 cars, their main components, and how they have evolved over time.
A Look Back: F1 Engines Over Time
Engines in Formula 1 have undergone significant changes over the decades. In the 1950s, cars utilized large, heavy engines that prioritized power. As the sport evolved, engines became smaller, lighter, and more powerful.
- In the 1980s, F1 saw turbocharged engines that produced extreme power. Some even reached more than 1,000 horsepower in qualifying.
- In the 1990s and early 2000s, V10 and V8 engines ruled the track. They were famous for their loud, high-pitched sound.
- From 2014 onward, Formula 1 moved to hybrid engines. These engines are less loud but smarter, mixing fuel power with electric energy.
This change showed F1’s push toward new technology and cleaner racing.
What Engine Does F1 Use Today?
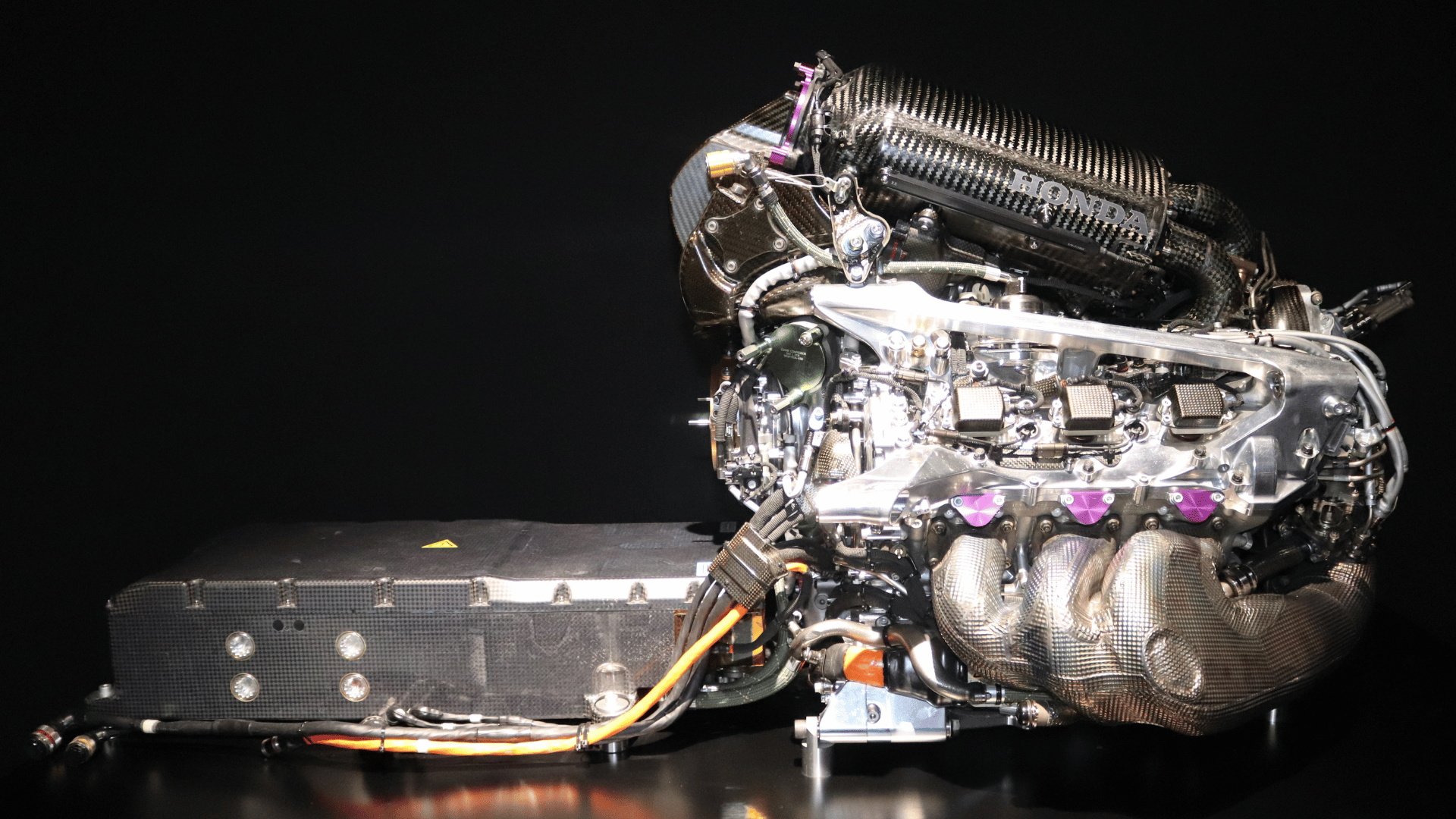
Image Source: Wikipedia
Today’s F1 cars use a 1.6-liter V6 turbo hybrid power unit. At first, the size may sound small, but the engine is very powerful. It can push out around 1,000 horsepower when combined with electric systems.
The current engines are designed to:
- Be very efficient with fuel.
- Deliver huge amounts of power.
- Last for several races before needing replacement.
- Reduce pollution compared to older engines.
Inside the Modern F1 Power Unit
Engines in Formula 1 are now called power units because they use both fuel and electricity. Different systems work together to give the car speed, save energy, and stay efficient. Each part helps make the car fast, reliable, and strong enough for long races.
Key Parts of the Engine
A Formula 1 power unit is made of several important parts:
- Internal Combustion Engine (ICE): The main part that burns fuel.
- Turbocharger: Pushes extra air into the engine for more power.
- MGU-H: Captures energy from hot exhaust gases and turns it into electricity.
- MGU-K: Collects energy during braking and stores it.
- Energy Store (Battery): Keeps the electric power until it is needed.
- Control Electronics: Works like the brain, making sure all systems work together.
Power and Performance
When all of these systems combine, an F1 car can produce about 1,000 horsepower.
That much power enables the car to reach 60 mph in under 2.5 seconds and achieve top speeds exceeding 220 mph.
These numbers are far beyond what most road cars can achieve.
Why Hybrid?
Formula 1 utilizes hybrid engines to strike a balance between speed and environmental care.
The hybrid systems save fuel, reduce pollution, and introduce new ideas that carmakers can later apply to normal road cars.
This makes Formula 1 not just fast but also forward-looking.
Team Engines in Formula 1
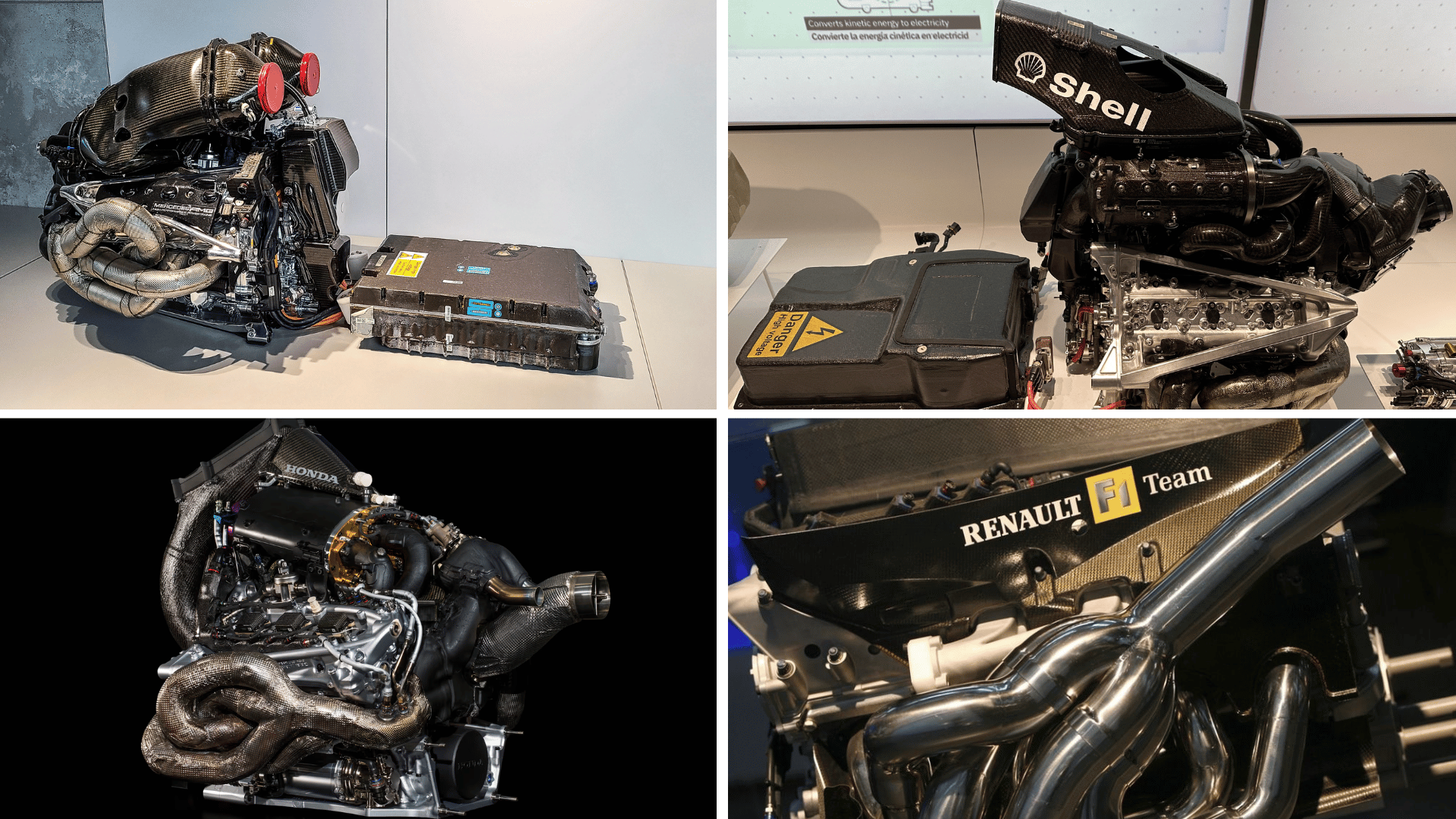
Engines play a huge role in Formula 1, and each team depends on strong partnerships with engine suppliers. Some teams build their own engines, while others rely on trusted suppliers. These choices affect speed, reliability, and overall performance on the track.
What Engine Does McLaren Use in F1
McLaren is one of the most famous names in Formula 1. Over the years, they have worked with many engine suppliers.
- 2015–2017: McLaren used Honda engines, which had problems with speed and reliability.
- 2018–2020: They switched to Renault engines. These were better, but still not top-level.
- Since 2021, McLaren has used Mercedes engines, a move that has given them more power and stronger results.
At present, McLaren uses the Mercedes-AMG F1 power unit in its cars.
McLaren F1 Engine Performance
The Mercedes engine gives McLaren a strong mix of power, speed, and reliability. It works well on fast tracks and tighter circuits, giving drivers confidence to push hard.
Since the switch to Mercedes power, McLaren has enjoyed more consistent results, including podium finishes.
The engine is also fuel-efficient, which helps with race strategy. While McLaren still faces tough rivals like Red Bull and Ferrari, the Mercedes unit provides a solid base.
With the right car design and driver skill, McLaren can keep fighting near the front
Other Teams and Their Engines Today
Below is a quick look at the engines used by other teams on the grid:
- Mercedes: Supplies its own team, McLaren, Aston Martin, and Williams.
- Ferrari: Supplies Ferrari, Haas, and Sauber (soon Audi).
- Honda/Red Bull Powertrains: Powers Red Bull and Racing Bulls.
- Renault (Alpine): Only makes engines for Alpine.
This mix illustrates how engine suppliers influence the grid and how some teams rely on the strength of others to remain competitive.
F1 Engines in 2026: Who Uses What?
Formula 1 will enter a new era in 2026. While the 1.6-liter V6 hybrid will remain, new fuel and electrical changes will reshape the sport. Teams are already planning their partnerships.
| Team | Engine in 2026 |
|---|---|
| Red Bull Racing | Red Bull Powertrains (with Ford support) |
| Racing Bulls (Toro Rosso) | Red Bull Powertrains (with Ford support) |
| McLaren | Mercedes-AMG |
| Aston Martin | Honda |
| Alpine | Mercedes |
| Ferrari | Ferrari |
| Haas | Ferrari |
| Williams | Mercedes |
| Audi (Sauber) | Audi |
| Cadillac (new team) | Ferrari (customer) |
Rules and Limits on Engines
Formula 1 engines are powerful but also heavily regulated. The FIA sets strict rules to keep racing fair, safe, and efficient. These rules control design, usage, and even cost.
FIA Engine Regulations
Formula 1 engines must follow clear standards:
- 1.6L V6 turbo hybrid: All teams must use this format.
- Fuel flow limit: Controls speed and improves efficiency.
- Engine use per season: Drivers can only use a limited number of engines; extra use leads to penalties.
- Safety and pollution standards: Engines must meet eco and safety requirements.
If a team breaks these rules, the FIA gives penalties, often in the form of grid drops.
Engine Lifespan and Cost
- Lifespan: Each engine is built to last about 7–8 races, despite being pushed to the limit every time.
- Cost: A single power unit can cost several million dollars. The high price comes from rare materials, advanced design, and long testing.
The Future of F1 Engines
The future of Formula 1 engines is focused on speed and sustainability. From 2026, the sport will keep the 1.6L V6 turbo hybrid but make big changes.
Cars will run on 100% sustainable fuel, and the hybrid system will provide even more electric power.
The complex MGU-H will be removed to simplify design and cut costs.
These updates aim to make racing greener while maintaining high performance, demonstrating how Formula 1 can lead the way in technology for both sports and road cars.
Conclusion
Engines are the heart of Formula 1 cars. They have changed from big, loud machines in the past to today’s smart hybrid power units.
Modern engines balance speed, fuel use, and technology, showing how far the sport has come.
Teams like McLaren depend on strong engines, with Mercedes power helping them stay competitive.
Looking ahead, 2026 will bring new fuel rules, stronger hybrid systems, and fresh engine suppliers like Audi and Cadillac.
These steps will keep Formula 1 fast while also moving toward a greener future. Engines will always decide who wins, who struggles, and who makes history on the track.
Want to learn more about F1 engines, teams, and racing updates? Stay tuned for more simple guides that break it all down.